What is Delta-8-THC?
- What is delta-8 THC & Is it legal?
- What are its medicinal benefits of delta-8 THC?
- Where does D8 THC comes from?
- How is it being used in medicine?
- What studies have been undertaken to determine its effects?
Delta-8 THC: Is it legal? What is it and what is it good for?
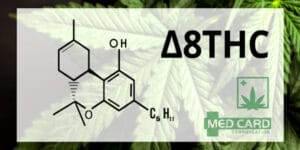
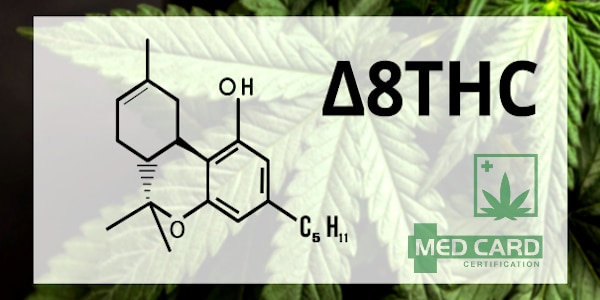
Delta-8 THC is a minor cannabinoid known to be an analog of delta-9 THC — the most abundant cannabinoid found in marijuana.
The molecular structures of the two cannabinoids are similar, albeit with some significant differences.
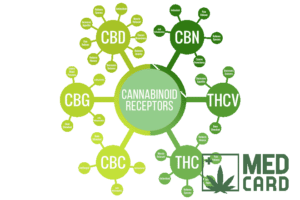
For starters, delta-8 THC has a far lower psychotropic effect than delta-9 THC. This might be due to the fact that, unlike D9 THC, D8 THC interacts with both the CB1 and CB2 receptors in the human endocannabinoid system (ECS). CBD, which also interacts with CB2 is known to reduce the psychotropic effects of THC.
Is delta-8 THC legal?
Up until recently, the legality of delta-8 THC fell into a gray area. This is due to the fact that it is produced in small enough quantities to qualify a cannabis cultivar as hemp (assuming total THCs remain under 0.3 percent).
However, according to the most recent DEA interim ruling, effective Aug. 20, any synthetically-produced THC is prohibited, regardless of the max 0.3 percent THC rule for hemp. The ruling specifically states: “All synthetically derived tetrahydrocannabinols [THCs] remain Schedule I controlled substances.”
However, a statement by the National Hemp Association claims that the issue of D8 THC is not addressed at all in the document as the compound is not “synthetically derived.” And one large supplier of D8 THC continues to sell the product and has announced that it is suing the DEA to void the ruling.
How D8 THC is treated under state laws is less confusing.
There are some cases in which D8 THC is clearly illegal such as in any state that has made all forms of cannabis and natural cannabinoids illegal.
However, in any state where cannabis is legal, D8 is also legal. And in states where medicinal use is legal, D8 is also legal for medicinal use.
We’ll be keeping an eye on this debate and will update our readers when a final ruling on the legalities of D8 THC is made available by the DEA.
How is delta-8 THC produced?
Delta-8 THC, unlike delta-9 THC, is not produced directly by cannabinoid-synthesizing enzymes in the plant. Rather, special breeding and molecular isolation are applied by growers and extractors to produce larger quantities of delta-8. It can be produced in both marijuana and hemp.
Because it is produced in such minute quantities (less than 0.3 percent) its presence in hemp flowers does not automatically disqualify a hemp crop from being legal. However, concentrated D8 THC falls into a legal gray area.
Medical Uses for Delta-8 THC
Although we have some basic knowledge of the medicinal benefits of the primary cannabinoids such as D9 THC and CBD, much less is known about the effects of minor cannabinoids such as D8 THC.
However, it is clear that both forms of THC have the ability to mitigate nausea, reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and stimulate appetite — all very valuable effects, especially for cancer patients.
As with D9 THC, D8 binds to the CB1 receptors located on the surface of neurons in the brain and central nervous system.
According to the National Cancer Institute:
“An analogue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) with antiemetic, anxiolytic, appetite-stimulating, analgesic, and neuroprotective properties. [Delta-8-THC] binds to the cannabinoid G-protein coupled receptor CB1, located in the central nervous system… This agent exhibits a lower psychotropic potency than [delta-9 THC], the primary form of THC found in cannabis.”
However, as mentioned, D8 THC also has an affinity for CB2 receptors, although less is known about this binding mechanism.
D8 THC is known to be approximately half as potent as Delta-9 THC as an intoxicant.
Moreover, D9 THC is far less stable and degrades easily. Because of its stability and limited psychotropic effects, D8 THC might be more desirable in some medical contexts.
Studies on delta-8 THC for pain relief and anti-inflammatory effects
A clinical study carried out in 1995 at Shaare Zedek Hospital in Jerusalem by Dr. Raphel Mechoulam indicated the efficacy of delta-8 THC in relieving nausea in children undergoing chemotherapy.
D8 THC was given to eight children ranging in ages from 3 to 13, all suffering from hematologic cancer. The children had been treated with various drugs and chemotherapy for the eight months leading up to the experimental treatment with D8 THC.
D8 THC treatments were administered two hours prior to each chemo session and continued every six hours for 24 hours. As a result of the treatment, vomiting was prevented and adverse side effects were almost non-existent.

Sign Up for Medical Cannabis Today!
For potential patients, if you’re ready, we make it easy to connect with a medical marijuana doctor nearby or online. If you are interested in getting certified, please fill out the MMJ patient registration form below and press submit to get started. See if you qualify today!

MedCard Registration Form